What is meant by catalytic converter ?...................
Catalytic converter:
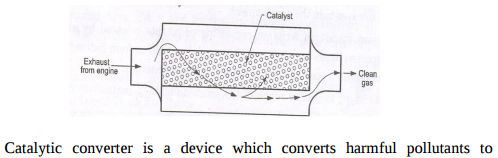
Catalytic converter:

(i) Swept Volume (VS) w.r.t I.C.Engine: The volume swept through by the piston in moving between top dead centre and bottom dead centre is called swept volume or piston displacement. It is denoted by VS. It is equal to the area of the piston multiplied by its stroke length. Therefore, Swept Volume = π/4xD2 xL
Where D = bore of the cylinder in m, and
L = stroke length in m.
(i) Indicated Power: The total power developed by combustion of fuel in the combustion chamber is called indicated power.
(ii) Brake Power: The power developed by an engine at the output shaft is called brake power.
(iii) Volumetric efficiency: It is defined as the ratio of the actual volume of the charge admitted into the cylinder to the swept volume of the piston is known as volumetric efficiency.
( iv) Brake specific fuel consumption: It is the mass of fuel consumed per kw developed per hour, and is a criterion of economical
Additives (1) Detergents – To keep engine parts, such as piston and piston rings, clean & free from deposits. (2) Dispersants – To suspend & disperse material that could form varnishes, sludge etc that clog the engine. (3) Anti – wear – To give added strength & prevent wear of heavily loaded surfaces such as crank shaft rods & main bearings. (4) Corrosion inhibitors – To fight the rust wear caused by acids moisture. Protect vital steel & iron parts from rust & corrosion.

Additives (any six ) (1) Detergents – To keep engine parts, such as piston and piston rings, clean & free from deposits. (2) Dispersants – To suspend & disperse material that could form varnishes, sludge etc that clog the engine. (3) Anti – wear – To give added strength & prevent wear of heavily loaded surfaces such as crank shaft rods & main bearings. (4) Corrosion inhibitors – To fight the rust wear caused by acids moisture. Protect vital steel & iron parts from rust & corrosion.
i) Indicated Power (ip) is defined as the power developed by combustion of fuel in the cylinder of engine. It is always more than brake power. ii) Mechanical efficiency : ηm : It is a measure of mechanical perfection of the engine or its ability to transmit power developed in the engine cylinder to the crank shaft . It is defined as the ratio of brake power to indicated power of the engine
Bharat stage III and IV norms :
Petrol Emission Norms (All figures in g/km) Emission Norm CO HC NOx HC+NOx PM BS-III 2.30 0.20 0.15 --- --- BS-IV 1.00 0.10 0.08 --- --- Diesel Emission Norms (All figures in g/km) Emission Norm CO HC NOx HC+NOx PM BS-III 0.64 --- 0.50 0.56 0.05 BS-IV 0.50 --- 0.25 0.30 0.025
The major air pollutants emitted by petrol & diesel engines are CO2, CO, HC, NOx, SO2, smoke & lead vapour. Effect of CO: Carbon monoxide combines with hemoglobin forming carboy hemoglobin ,which reduces oxygen carrying capacity of blood. This leads to laziness, exhaustion of body & headache. Prolong exposure can even leads to death. It also affects cardiovascular system, thereby causing heart problem Effect of CO2: Causes respiratory disorder & suffocation.

