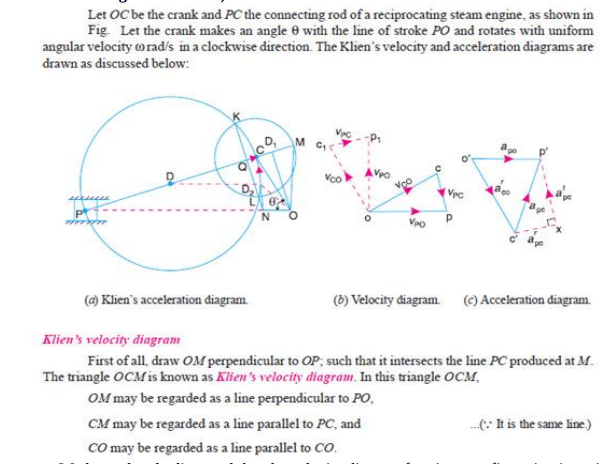
Explain the Klein's construction to determine velocity and acceleration of single slider crank mechanism.

Linear Velocity: It may be defined as the rate of change of linear displacement of a body with respect to the time. Since velocity is always expressed in a particular direction, therefore it is a vector quantity. Mathematically, linear velocity, v = ds/dt
Angular Velocity: It may be defined as the rate of change of angular displacement with respect to time. It is usually expressed by a Greek letter ɷ (omega). Mathematically, angular velocity, ɷ = dƟ /dt
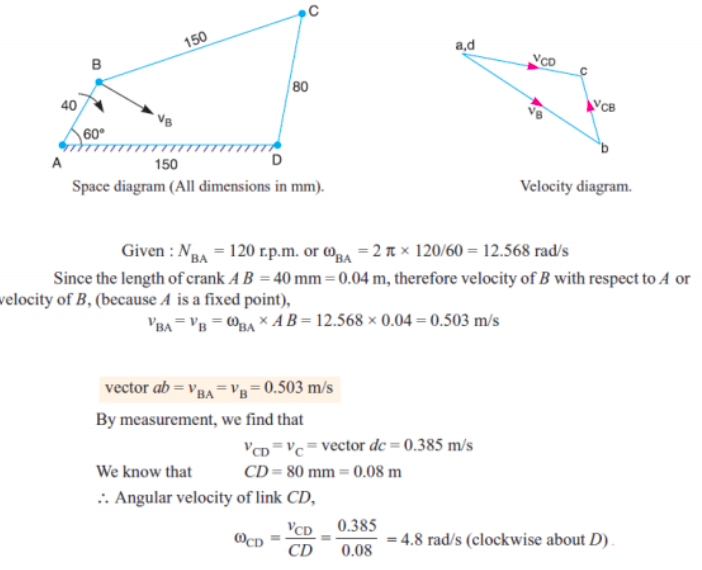
Velocity of point B & C :
Vb = AB x wAB = 0.35 x 50 = 17.5 m/s
Vc = AC x wAB = 0.175 x 50 = 8.75 m/s
Construction :
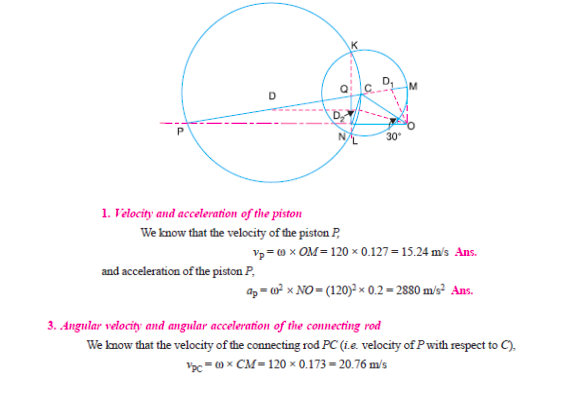
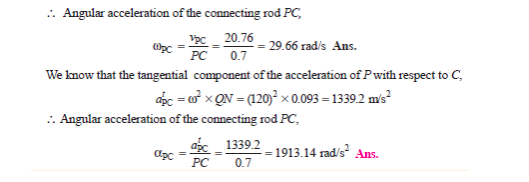
Given: Crank AB = 20 mm = 0.02 m, C. R. BC = 80 mm = 0.08 m
N = 1000 rpm, ωBA= 2πN/60 = 2π x 1000/60 = 104.7 rad/sec
VBA = ωBA x AB = 104.7 x 0.02 = 2.09 m/s
From velocty diagram: Velocity of C w.r.t. B -
VCB = vector cb = 1.15 m/s
Angular velocity of Connecting rod ‘BC’ ωCB = VCB / CB = 1.15/0.08 = 14.375 rad /sec
Velocity of slider ‘C’
VC= vector ac = 2 m/sec
i) Velocity of slider:
Vp = w.r [sinθ + sin2θ/2n ]
where,
Vp - velocity of slider
w- angular velocity
θ – angle of crank to line of stroke ‘PO’
n- l/r = ratio of length of connecting rod to crank radius.
ii) Acceleration of slider:
fp = w2 r(cos θ + cos2θ/n)
where, fp – acceleration of slider
iii) Angular velocity of connecting rod.: