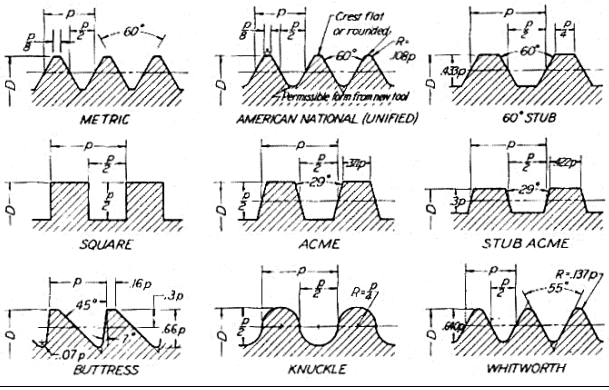
Draw the different thread profiles used for power screws.(Draw any four thread profiles)

i) Types of gear trains 1) Simple gear train 2) Compound gear train 2) Epicyclic gear train 4) Inverted gear train Simple gear train. When there is only one gear on each shaft, it is known as simple gear train. The gears are represented by their pitch circles. When the distance between the two shafts is small, the two gears are made to mesh with each other to transmit motion from one shaft to the other Epicyclic gear train: A simple epicyclic gear train is shown in Fig. where a gear A and the arm C have a common axis at O1about which they can rotate.

Advantages of chain drive over belt drive (Any four)
a) No slip takes place in chain drive as in belt drive there is slip.
b) Occupy less space as compare to belt drive.
c) High transmission efficiency.
d) More power transmission than belts drive.
e) Operated at adverse temperature and atmospheric conditions.
f) Higher velocity ratio.
g) Used for both long as well as short distances.
Disadvantages of chain drive: 1. Manufacturing cost of chains is relatively high
Define slip and creep in the belt drive Slip --- Slip is defined as insufficient frictional grip between pulley (driver/driven) and belt. Slip is the difference between the linear velocities of pulley (driver/driven) and belt. Creep ----- Uneven extensions and contractions of the belt when it passes from tight side to slack side. There is relative motion between belt and pulley surface, this phenomenon is called creep of belt.

Application of Belts: 1. V- Belt drive – In I.C. Engine power transmission from crankshaft pulley to water pump pulley. 2. Flat Belt drive – Floor mill 3. Chain drive – motor cycle 4. Gear drive – In automotive gear boxes
Types of Chains & Sprockets: The chains, on the basis of their use, are classified into the following three groups : 1. Hoisting and hauling (or crane) chains, 2. Conveyor (or tractive) chains, and 3. Power transmitting (or driving) chains. Sprockets: 1. Taper lock sprockets 2.Pilot bore sprocket 3.Platewheel sprocket
Gearing law states that, "The law of gearing states that the angular velocity ratio of all Gears of a meshed gear system must remain constant also the common normal at the point of contact must pass through the pitch point."
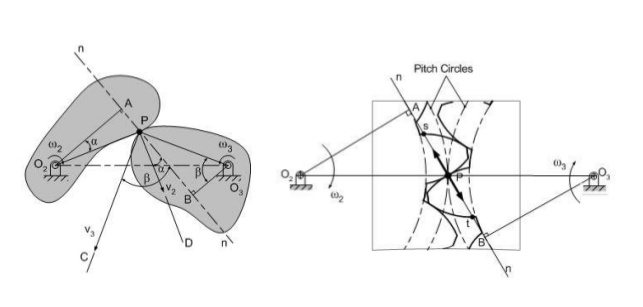
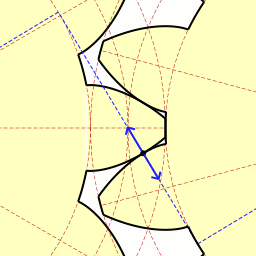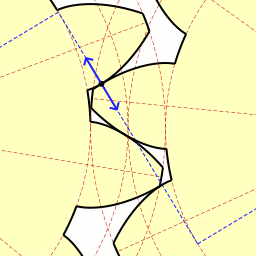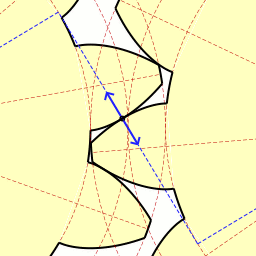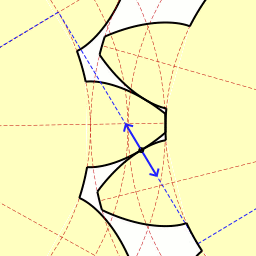
Definition: When two or more gears are made to mesh with each other to transmit power from one shaft to another. Such a combination is called gear train
Purpose: The purpose of the train used is
To obtain correct & required velocity ratio between driver & driven shafts.
To decide upon the relative position of the axes of shafts.
To decide upon amount of power to be transmitted between shafts
Types: Following are the different types of gear trains, depending upon the arrangement of wheels :