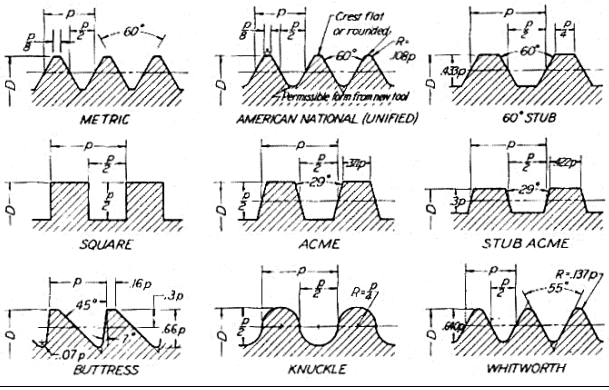
Draw the different thread profiles used for power screws.(Draw any four thread profiles)


The life of an individual bearing is defined as the total number of revolutions (or the number of hours at a given constant speed) which the bearing can complete before the evidence of fatigue failure develops on the balls or races. The bearing life can be defined by rating life. The rating life of a group of apparently identical bearing is defined as the number of revolutions (or the number of hours at a given constant speed) that 90 percent of a group of bearings will complete or exceed before the first evidence of fatigue failure develops. It is also known as L10 life.
(i) A knuckle joint is used to connect two rods which are under the action of tensile loads. However, if the joint is guided, the rods may support a compressive load. (ii) Its use may be found in the link of a cycle chain, tie rod joint of roof truss, valve rod joint with eccentric rod, pump rod joint, tension link in bridge structure and lever and rod connections of various types.
Ergonomics is defined as the scientific study of the man – machine working environment relationship and the application of anatomical, physiological, psychological principles to solve the problems arising from this relationship.
When a machine part is subjected to a constant stress at high temperature for a long period of time, it will undergo a slow and permanent deformation called ‘creep’. This property is considered in designing internal combustion engines, boilers and turbines
(i) Dead or steady load (ii) Live or variable load (iii) Suddenly applied or shock load (iv) Impact load
(i) FeE220: Steel having yield strength of 220 N/mm2 . (ii) 20C8 : Carbon steel containing 0.15 to 0.25 percent (0.2 percent on average) carbon and 0.60 to 0.90 percent (0.80 percent on average) manganese.
Machine design is the process of selection of the materials, shapes, sizes and arrangements of
mechanical elements so that the resultant machine will perform the prescribed task. OR
Machine Design is the creation of new and better machines and improving the existing ones
Data: Initial tension, To = 2000 N, coefficient of friction, µ = 0.3, Angle of lap, θ = 1500 = 1500 x П / 180 = 2.618 rad, Smaller pulley radius, R = 200 mm, hence, D = 400 mm, Speed of smaller pulley, N = 500 r.p.m. We know that the velocity of the belt, v = П = П = 10.47 m/sec (01 mark) Let T1 = Tension in the belt on the tight side, N Let T2 = Tension in the belt on the slack side, N We know that, T0 = Hence, 2000 = (T1 + T2) / 2 Thus, (T1 + T2) = 4000 N ....................... (1) We also know that, = therefore, = or = 2.2 .............
Roller follower is preferred over knife edge follower Knife-edge of the follower will cause the wear of the cam. Higher load on the small contact area the follower likely to cause wear at the tip of Knifeedge due to more stresses. Knife-edge follower practically not feasible for higher torque / load applications. More friction due to sliding motion of the knife-edge follower and hence, more maintenance. Roller follower on the other hand produces smooth operation with less wear and tear of both cam and follower.