Q.1. Explain working of Four Stroke SI(Petrol) Engine
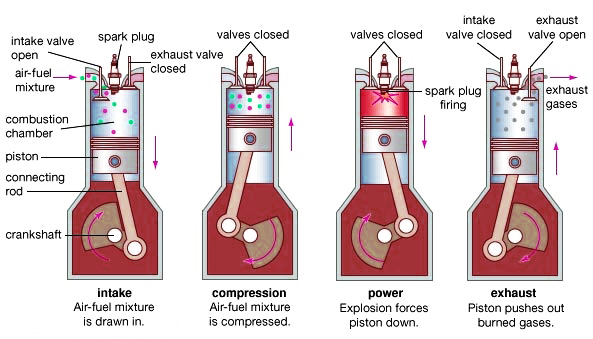
1. Suction stroke:- During this stroke the crank moves from TDC to BDC. The piston moves downward. inlet valve is open and exhaust valve is closed. The charge is sucked into cylinder. Stroke continues till piston reaches BDC ,as shown in fig
2. Compression stroke:- In this stroke both inlet and exhaust valves are closed and charge is compressed as the piston moves upward from BDC to TDC. As result of compression, the pressure and temperature of charge is increased considerably. This completes one revolution of crankshaft. The compression stroke is shown in fig.
3. Expansion or power stroke:- Shortly before the piston reaches TDC the charge is ignited with the help of spark plug. It suddenly increases temperature and pressure in the cylinder with constant volume. That pressure pushes piston downward. Hot burned gases expands due to high speed of piston. Thus the heat energy is converted into mechanical energy. In this stroke both valves are closed and piston moves from TDC to BDC.
4. Exhaust stroke:- In this stroke exhaust valve is open and piston moves from BDC to TDC. This movement of piston pushes out products of combustion from cylinder. This completes the second revolution and one cycle .
VIDEOS FOR UNDERSTANDING
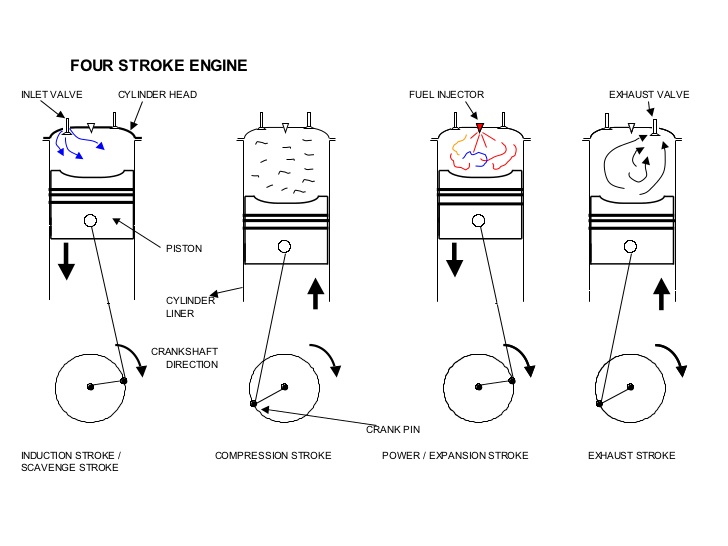
Q.2 . Explain working of Four Stroke CI (Diesel) Engine
WORKING IS SAME AS SI ENGINE EXCEPT FOLLOWING CHANGES
Spark plug is replaced by Injector, Charge(air+fuel) is replaced by air only
Spark ignition is replaced by Fuel Injection
Q.3. Compare SI engine with CI engine
|
Point |
Petrol engine (S.I) |
Diesel engine (C.I) |
|
1. Air fuel |
Air fuel mixture is inducted into cylinder |
Only air is inducted into cylinder |
|
2. Fuel supply |
Carburetor is used to mix air and petrol in the required proportion and to supply to the engine during |
The injector is employed to inject fuel at the end of compression stroke |
|
3. Pressure |
Pressure at the end of compression is about 10 bar |
Pressure at end of compression is about 35 bar |
|
4. Ignition |
The charge is ignited with the help of spark plug |
The fuel is injected in the form of fine spray. Which gets auto-ignited. |
|
5. Compression ratio |
6 to 10 |
15 to 25 |
|
6. Weight |
As compression ratio is low weight of engine is less. |
As the compression ratio is high the diesel engines are heavier. |
|
7. Running cost |
The running cost of petrol engine is high because of higher cost of petrol |
The running cost of diesel engine is low because of lower cost of diesel |
|
8. Thermal efficiency |
The thermal efficiency is about 26% |
The thermal efficiency is about 40% |
|
9.Noise and vibration |
Less noise and vibration |
More noise and vibration |
|
10.Applications |
It is used in motorcycles and light motor vehicles,sporting vehicles |
It is used in heavy duty vehicles and earth moving equipments and for power plants. |
Q.4. Compare two stroke and four stroke engine.
|
Point |
Four stroke |
Two stroke |
|
1. No. of strokes |
Cycle is completed in four strokes (Two Rev) |
cycle is completed in two strokes (1rev.)
|
|
2. Power stroke |
One power stroke every two rev. |
One power stroke in each revolution
|
|
3. Valves |
It has valve mechanism |
It has no valves.( it has ports) |
|
4. Weight |
It is heavier that 2 stroke |
It is light weight |
|
5. Piston |
Piston is flat or dome shaped |
Piston has deflector |
|
6. Flywheel |
Heavy flywheel is required because of more fluctuation. |
Lighter flywheel is required due to less energy fluctuation. |
|
7. Thermal efficiency |
High thermal efficiency |
Low thermal efficiency |
|
8.Maintenance |
Maintenance is complicated |
Maintenance low |
|
9. Cost |
Higher cost |
Lower cost |
|
10. Applications |
Used where efficiency is important ex. Trucks,buses,bikes |
Used where more power is required in small size ex. Scooter, Motor boats |
- Log in to post comments
