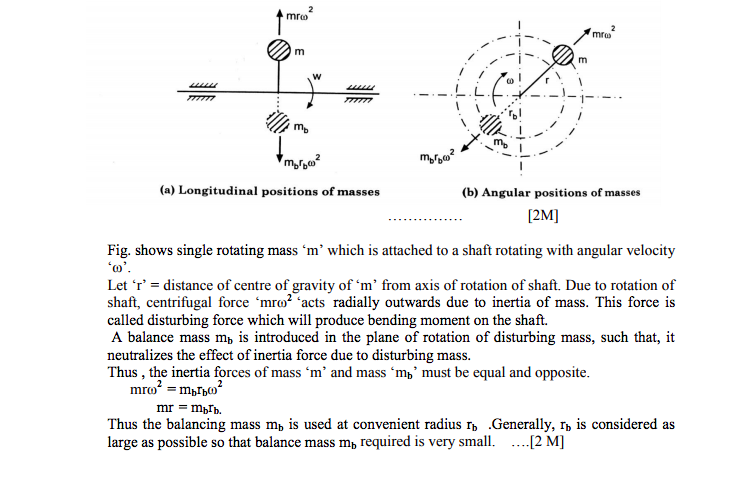
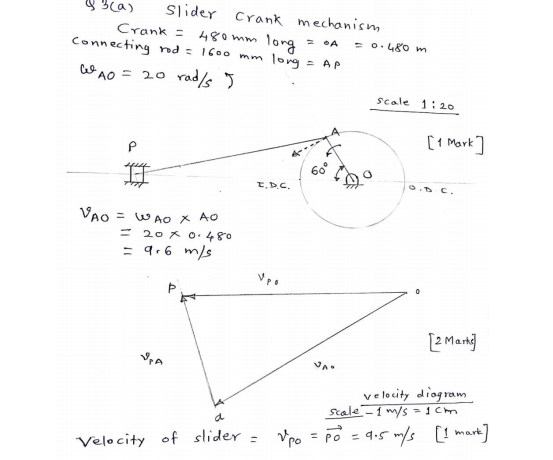
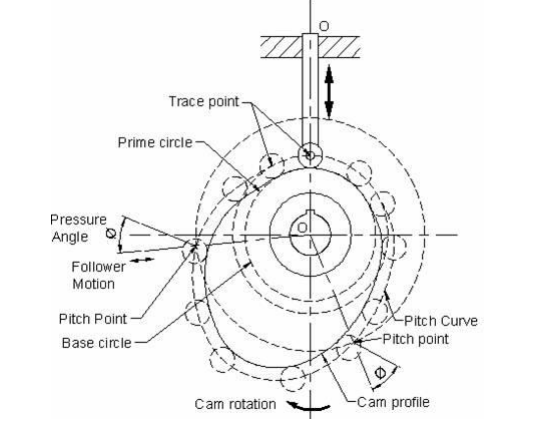
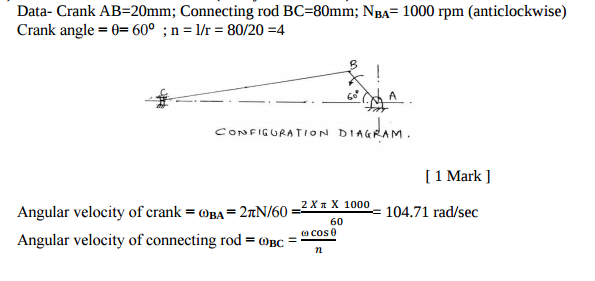
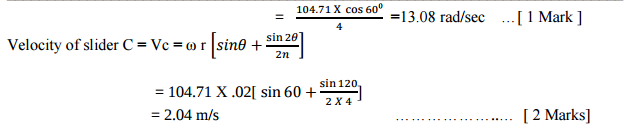What are the different types of follower motion ? Also draw displacement diagram for uniform velocity.
Different types of follower motions –
The follower during its travel may have one of the following motions:-
Uniform velocity, Simple harmonic motion, Uniform acceleration and retardation, Cycloidal motion.
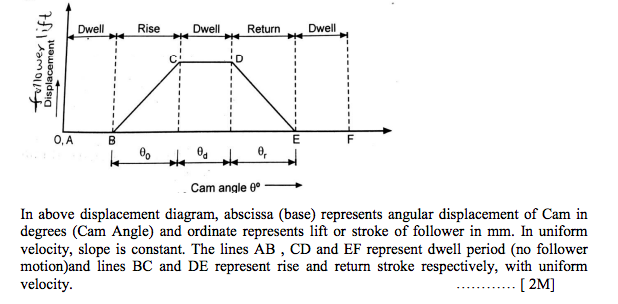
Displacement Diagram of Uniform Velocity: