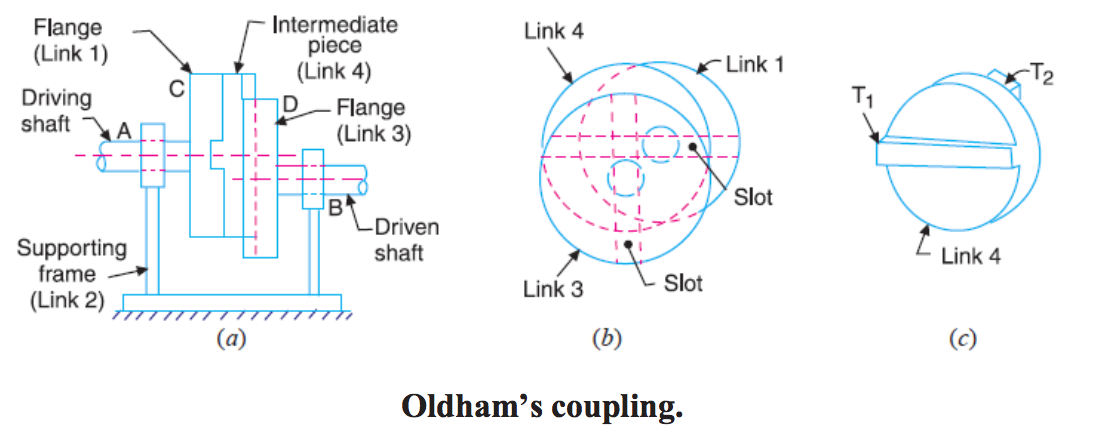
Draw the neat labeled sketch of Oldham’s coupling. State its applications.
Applications:
An Oldham's coupling is used for connecting two parallel shafts whose axes are at a small distance apart.
Used to transmit motion and power.
Applications:
An Oldham's coupling is used for connecting two parallel shafts whose axes are at a small distance apart.
Used to transmit motion and power.

Types of Constrained Motions :
Following are the three types of constrained motions:
In an epicyclic gear train, the axes of the shafts, over which the gears are mounted, may move relative to a fixed axis. A simple epicyclic gear train is shown in Fig. where a gear A and the arm C have a common axis at 1 about which they can rotate. The gear B meshes with gear A and has its axis on the arm at O2, about which the gear B can rotate. If the arm is fixed, the gear train is simple and gear A can drive gear B or viceversa, but if gear A is fixed and the arm is rotated about the axis of gear A (i.e.
(i) Uniform pressure theory:
When the mating component in clutch, bearing are new, then the contact between
surfaces may be good over the whole surface.
It means that the pressure over the rubbing surfaces is uniform distributed.
This condition is not valid for old clutches, bearings because mating surfaces may
have uneven friction.
The condition assumes that intensity of pressure is same.
P = W/A =Constant; where, W= load, A= area
(ii) Uniform wear theory in clutches and bearings:
Inversions of double slider crank chain:
i.Scotch Yoke mechanism.
ii.Oldham’s coupling.
iii. Elliptical trammel.