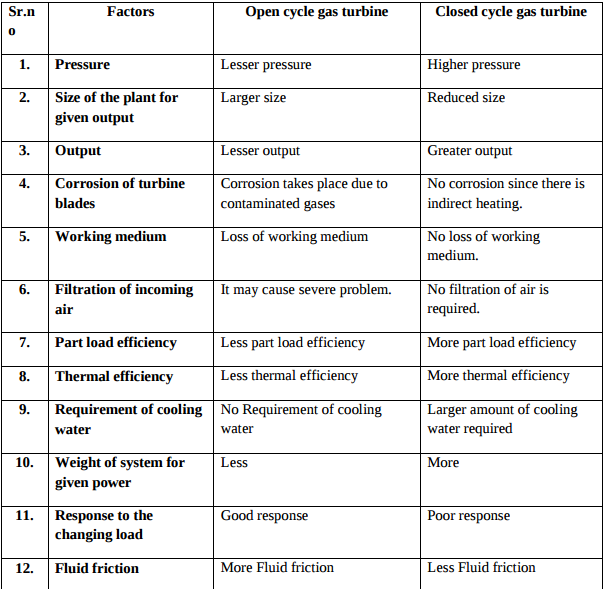
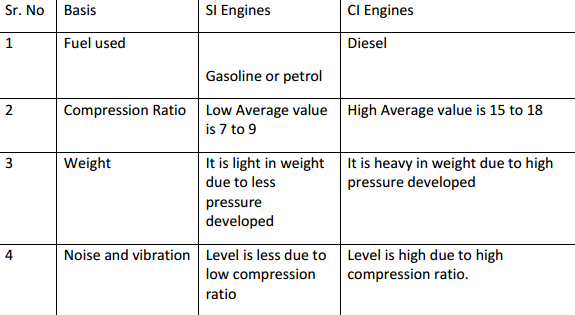
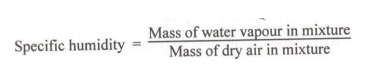State the norms of Bharat stage III and IV
Bharat stage III and IV norms :
Petrol Emission Norms (All figures in g/km) Emission Norm CO HC NOx HC+NOx PM BS-III 2.30 0.20 0.15 --- --- BS-IV 1.00 0.10 0.08 --- --- Diesel Emission Norms (All figures in g/km) Emission Norm CO HC NOx HC+NOx PM BS-III 0.64 --- 0.50 0.56 0.05 BS-IV 0.50 --- 0.25 0.30 0.025