Explain with neat sketch working principle of any one type of catalytic converter.

Methods to determine the frictional power of I.C. engine are`
1. Willan’s line method 2. Morse test 3. Motoring test 4. Difference between i.p. and b.p.
Explanation of any one method
Superimposed P-V Diagram of Otto, Diesel & Duel Cycle: A comparison of the cycles (Otto, Diesel and Dual) on the p-v and T-s diagrams for the same compression ratio and heat supplied is shown in the Fig. Since all the cycles reject their heat at the same specific volume, process line from state 4 to 1, the quantity of heat rejected from each cycle is represented by the appropriate area under the line 4 to 1 on the T-s diagram. As is evident from the cycle which has the least heat rejected will have the highest efficiency.
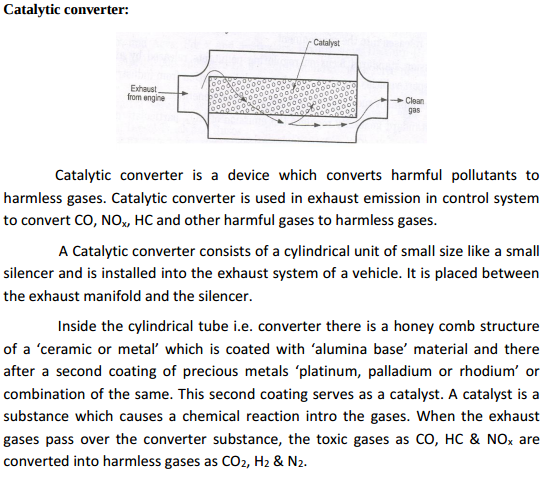
Catalytic converter:
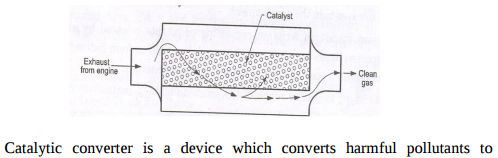
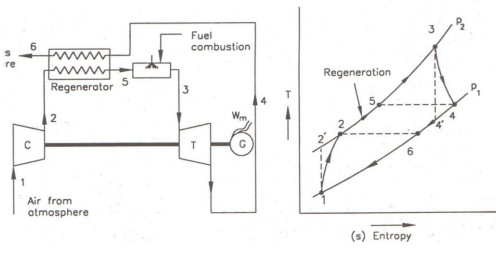
Regenerative method to improve thermal efficiency in gas turbines : The exhaust gases a lot of heat as their temperature is far above the ambient temperature . The heat of exhaust gases can be used to heat the air coming from the compressor thus reducing the mass of the fuel supplied in the combustion chamber as shown in the figure. This method is called regenerative method.
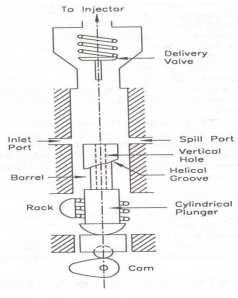
Fuel injection pump : Fuel injection pump is used widely for the supply of fuel under high pressure in diesel engines
Additives (any six ) (1) Detergents – To keep engine parts, such as piston and piston rings, clean & free from deposits. (2) Dispersants – To suspend & disperse material that could form varnishes, sludge etc that clog the engine. (3) Anti – wear – To give added strength & prevent wear of heavily loaded surfaces such as crank shaft rods & main bearings. (4) Corrosion inhibitors – To fight the rust wear caused by acids moisture. Protect vital steel & iron parts from rust & corrosion.
i) Indicated Power (ip) is defined as the power developed by combustion of fuel in the cylinder of engine. It is always more than brake power. ii) Mechanical efficiency : ηm : It is a measure of mechanical perfection of the engine or its ability to transmit power developed in the engine cylinder to the crank shaft . It is defined as the ratio of brake power to indicated power of the engine
Non dispersive infra red gas analyzer ( NDIR) : The working principle of infra red gas exhaust gas analyzer is as shown in figure . It works on the principle of hetero atomic gases absorbs infra red energy at distinct and separated wavelength. The absorbed energy raises the temperature and pressure of confined gas. This enables to measure contents of hydro carbon and carbon monoxide. This is a faster method of gas analysis. The standard sample is filled in reference cell R . the sample of gas under testing is filled in cell S .
