By user |
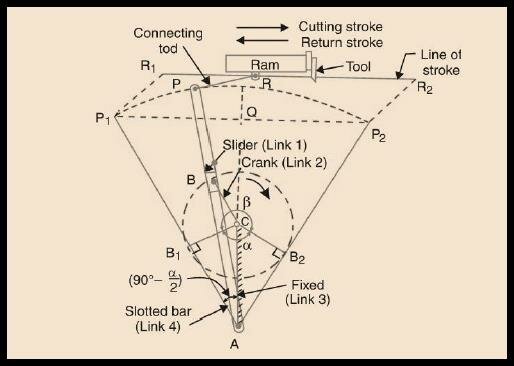
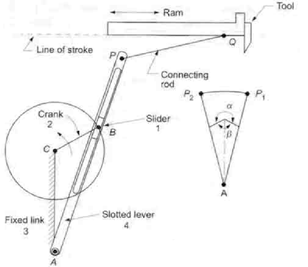
Q17: Explain with Sketch the Crank and Slotted Lever Quick Return Mechanism Used in a Shaping Machine
Introduction
The crank and slotted lever quick return mechanism is one of the most widely used mechanisms in shaping machines, slotting machines, and sometimes mechanical presses.
Its main purpose is to convert rotary motion into reciprocating motion with a quick return stroke, making metal cutting more efficient.
Construction / Components
The mechanism consists of the following main parts:
- Driving Crank
- Connected to a rotating shaft.
- Provides continuous rotary motion.
- Slotted Lever (Link)
- A long link with a slot in which the crank pin moves.
- Converts rotary motion into oscillatory motion.
- Ram or Slider
- Performs the cutting stroke and return stroke.
- Frame / Fixed Link
- Acts as support and provides the pivot to the slotted lever.
- Connecting Rod
- Transfers oscillatory motion of slotted lever to the ram.
Working Principle
The mechanism works on the principle of non-uniform angular velocity during rotation, which produces a longer cutting stroke and a shorter return stroke.
Working Steps
- The crank rotates uniformly by a motor.
- The crank pin slides inside the slot of the slotted lever.
- As the crank rotates:
- One half of rotation causes forward (cutting) stroke.
- The other half causes return stroke.
- Because of geometry, the return stroke takes less time, creating the quick return effect.
This increases machine productivity.
Quick Return Ratio

This ratio is always greater than 1, indicating faster return movement.
Application in Shaping Machine
In a shaping machine:
- The ram carries the cutting tool.
- During forward stroke, metal is cut.
- During return stroke, no cutting takes place.
- Therefore, return stroke must be faster → mechanism saves time.
- Log in to post comments