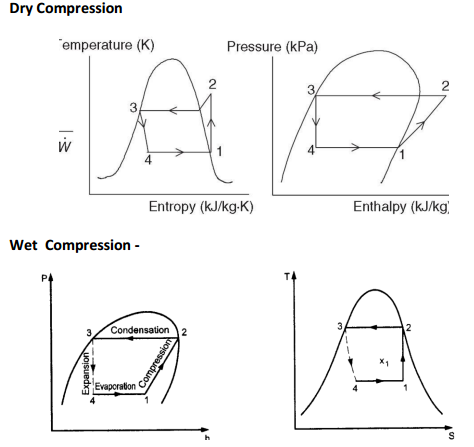
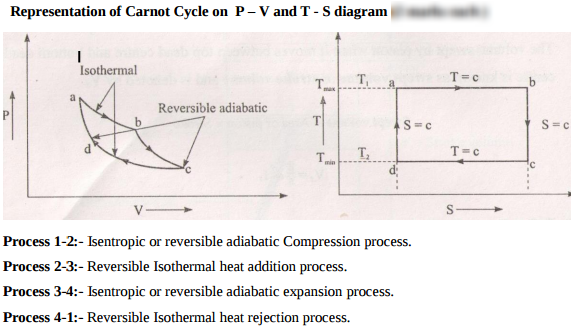
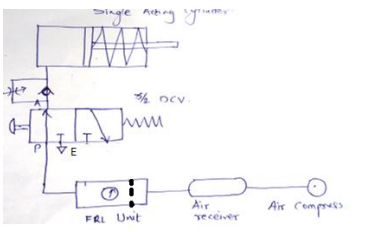
Design of Levers : Hand Lever, Foot Lever, Bell crank lever
Design of levers
Key points to remember regarding design of levers :
- the design of levers is all about finding the dimensions of the levers so that it could perform its function satisfactorily
- A lever is force multiplier, depending upon the location of the load and effort from the fulcrum point.
- Levers are classified on the basis of location of load, effort and fulcrum point.
- Log in to post comments