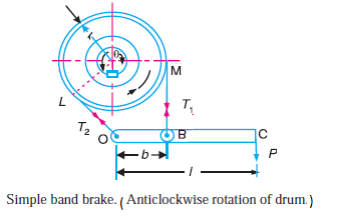
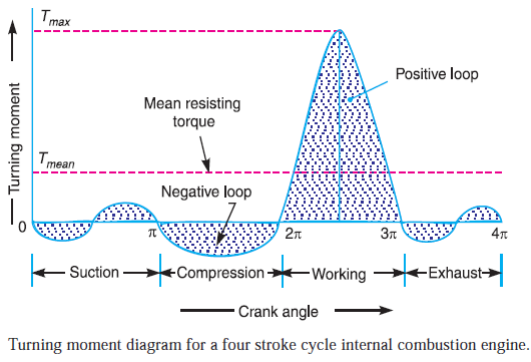
Define the sensitivity in relation to governer. State its significance.
The function of governor is to regulate the mean speed of the engine, when there are variations in the load. Governor automatically adjusts and controls the supply of fuel / working fluid to the engine with the varying load conditions and keeps the mean speed within the certain desired limits. e.g. When the load on an engine increases, its speed decreases, therefore it becomes necessary to increase the supply of fuel or working fluid. The configuration of the governor changes and valve is moved to increase the supply of working fluid. Conversely, when the load on the engine