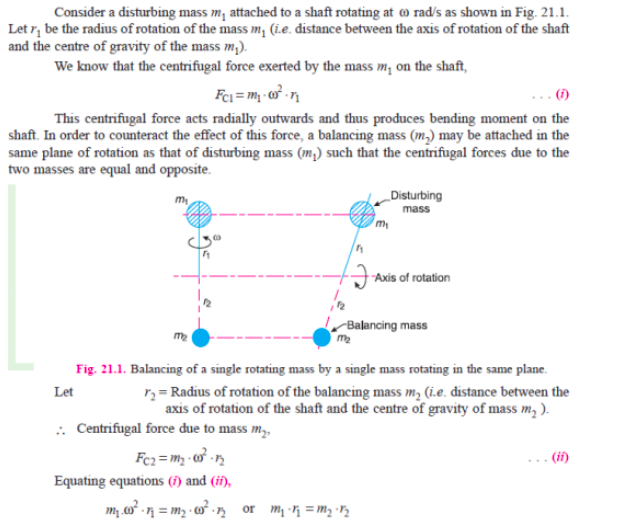
Procedure for balancing single rotating mass when its balancing mass is rotating in same plane:

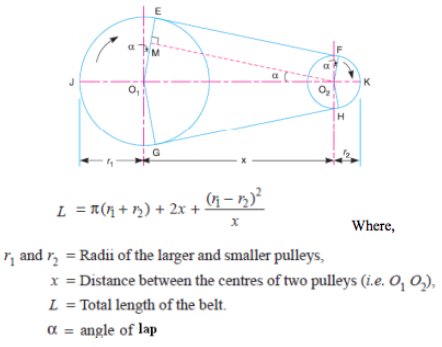
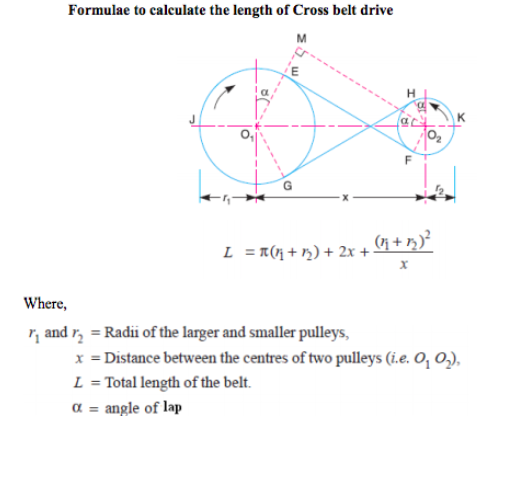
Formulae to calculate the length of open belt drive :
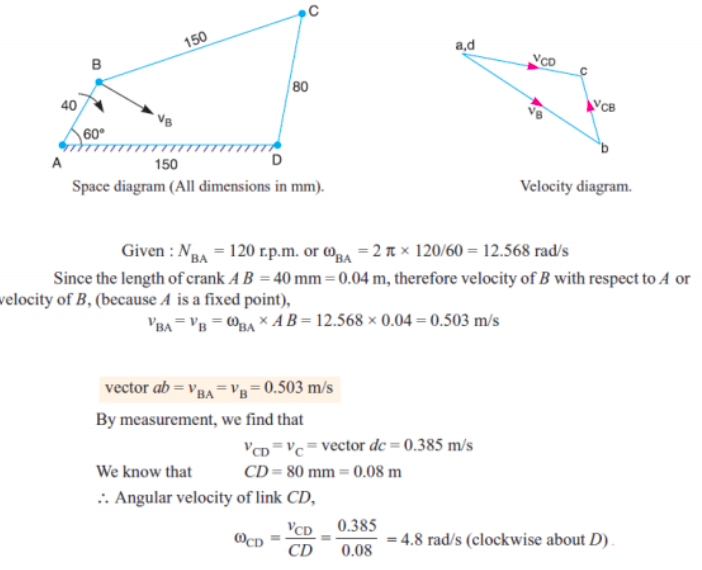
Given: Crank AB = 20 mm = 0.02 m, C. R. BC = 80 mm = 0.08 m
N = 1000 rpm, ωBA= 2πN/60 = 2π x 1000/60 = 104.7 rad/sec
VBA = ωBA x AB = 104.7 x 0.02 = 2.09 m/s
From velocty diagram: Velocity of C w.r.t. B -
VCB = vector cb = 1.15 m/s
Angular velocity of Connecting rod ‘BC’ ωCB = VCB / CB = 1.15/0.08 = 14.375 rad /sec
Velocity of slider ‘C’
VC= vector ac = 2 m/sec
i) Trace point : It is a reference point on the follower and is used to generate the pitch curve. In case of knife edge follower, the knife edge represents the trace point and the pitch curve corresponds to the cam profile. In a roller follower, the centre of the roller represents the trace point.
i) Velocity of slider:
Vp = w.r [sinθ + sin2θ/2n ]
where,
Vp - velocity of slider
w- angular velocity
θ – angle of crank to line of stroke ‘PO’
n- l/r = ratio of length of connecting rod to crank radius.
ii) Acceleration of slider:
fp = w2 r(cos θ + cos2θ/n)
where, fp – acceleration of slider
iii) Angular velocity of connecting rod.:
Applications:
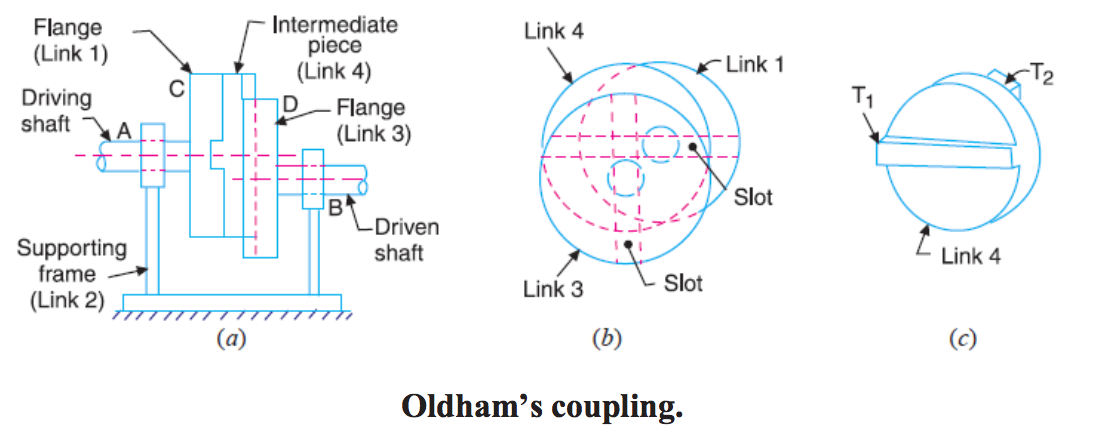
An Oldham's coupling is used for connecting two parallel shafts whose axes are at a small distance apart.
Used to transmit motion and power.
Types of Constrained Motions :
Following are the three types of constrained motions:
In an epicyclic gear train, the axes of the shafts, over which the gears are mounted, may move relative to a fixed axis. A simple epicyclic gear train is shown in Fig. where a gear A and the arm C have a common axis at 1 about which they can rotate. The gear B meshes with gear A and has its axis on the arm at O2, about which the gear B can rotate. If the arm is fixed, the gear train is simple and gear A can drive gear B or viceversa, but if gear A is fixed and the arm is rotated about the axis of gear A (i.e.
Necessity: A clutch is necessary for the transmission of power of shafts and machines which must be started and stopped frequently. Its application is also found in cases in which power is to be delivered to machines partially or fully loaded. The force of friction is used to start the driven shaft from rest and gradually brings it up to the proper speed without excessive slipping of the friction surfaces.
In automobiles, friction clutch is used to connect the engine to the driven shaft. It may be noted that -