State any two types of motion of the follower.
The follower during its travel may have one of the following motions.
1. Uniform velocity,
2. Simple harmonic motion,
3. Uniform acceleration and retardation,
4. Cycloidal motion.
The follower during its travel may have one of the following motions.
1. Uniform velocity,
2. Simple harmonic motion,
3. Uniform acceleration and retardation,
4. Cycloidal motion.
1. Mechanism : When one of the links of a kinematic chain is fixed, the chain is known as mechanism.
2. Inversion of mechanism The method of obtaining different mechanisms by fixing different links in a kinematic chain, is known as inversion of the mechanism. So we can obtain as many mechanisms as the number of links in a kinematic chain by fixing, in turn, different links in a kinematic chain.
The high speed of engines and other machines is a common phenomenon now-a-days. It
is, therefore, very essential that all the rotating and reciprocating parts should be completely
balanced as far as possible. If these parts are not properly balanced, the dynamic forces are set
up. These forces not only increase the loads on bearings and stresses in the various members, but
also produce unpleasant and even dangerous vibrations. The balancing of unbalanced forces is
(i) Disc brake: Used in two wheelers as well as in four wheelers.
(ii) Internal expanding brake: Used in motor cars, light trucks, two wheelers etc.
Disadvantages of chain drives:
1. Manufacturing cost of chains is relatively high.
2. The chain drive needs accurate mounting and careful maintenance.
3. High velocity fluctuations especially when unduly stretched.
4. Chain operations are noisy as compared to belts.
(i) Coefficient of fluctuation of speed: Coefficient of fluctuation of speed is defined as the ratio of the maximum fluctuation of speed to the mean speed. It is denoted by C s.
Mathematically,
C s = (N 1 – N 2 ) /N
Where, N 1 = maximum speed in rpm;
N 2 =minimum speed in rpm; N = mean speed in rpm
Classification of drives:
(i) Belt drives.
(ii) Chain drives.
(iii) Rope.
(iv) Gear drives.
(i) Pressure angle: It is the angle between the direction of the follower motion and a normal to the pitch curve. This angle is very important in designing a cam profile. If the pressure angel is too large, a reciprocating follower will jam in its bearing.
(ii) Pitch point: It is point on pitch curve having the maximum pressure angle.
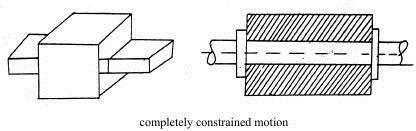
Types of constrained motion:
(i)Completely constrained motion.
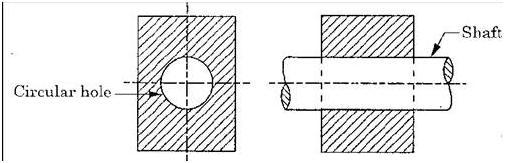
(ii)Incompletely constrained motion.
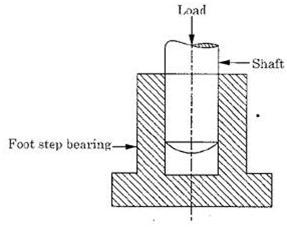
(iii)Successfully constrained motion.