Define i) Humidity ratio, ii) Specific humidity
Specific humidity : It is defined as the ratio of mass of vapor to the mass of dry air in a given sample of moist air . It is denoted by ω
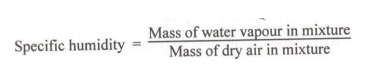
Specific humidity : It is defined as the ratio of mass of vapor to the mass of dry air in a given sample of moist air . It is denoted by ω
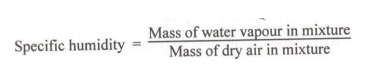
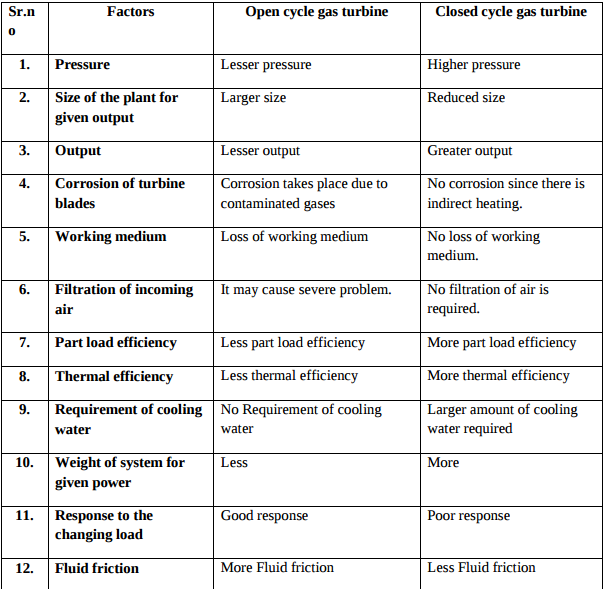
Open cycle and closed cycle gas turbines Any four differences
The major air pollutants emitted by petrol & diesel engines are CO2, CO, HC, NOx, SO2, smoke & lead vapour. Effect of CO: Carbon monoxide combines with hemoglobin forming carboy hemoglobin ,which reduces oxygen carrying capacity of blood. This leads to laziness, exhaustion of body & headache. Prolong exposure can even leads to death. It also affects cardiovascular system, thereby causing heart problem Effect of CO2: Causes respiratory disorder & suffocation.



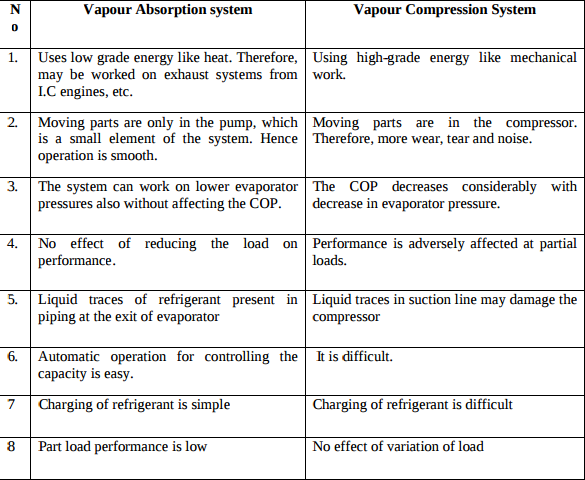
Differences between Vapour Absorption and Vapour Compression refrigeration system
Non dispersive infra red gas analyzer ( NDIR) : The working principle of infra red gas exhaust gas analyzer is as shown in figure . It works on the principle of hetero atomic gases absorbs infra red energy at distinct and separated wavelength. The absorbed energy raises the temperature and pressure of confined gas. This enables to measure contents of hydro carbon and carbon monoxide. This is a faster method of gas analysis. The standard sample is filled in reference cell R . the sample of gas under testing is filled in cell S .

Lobe type air compressor: it is a rotary type of compressor consisting of two rotors which are driven externally. One rotor is connected to drive and second is connected to gear. These two rotors have two or three lobes having epicycloids, hypocycloid or involutes profiles. In the figure two lobes compressor is shown with a inlet arrangement and receiver. A very small clearance is maintained between surfaces so that wear is prevented. Air leakage through this clearance decreases efficiency of this compressor.
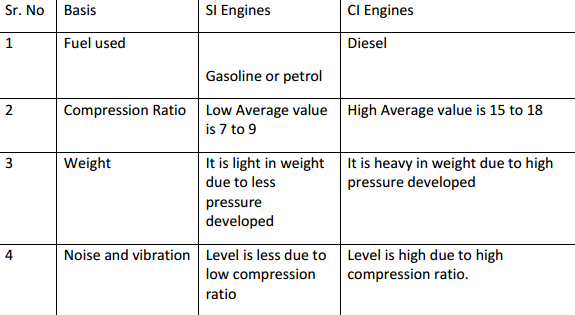
Difference between SI and CI engines