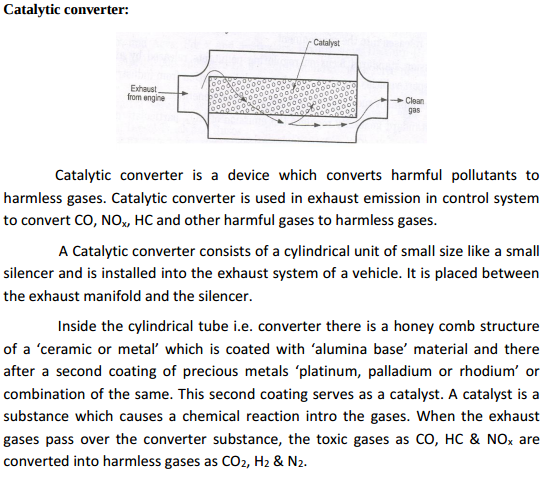
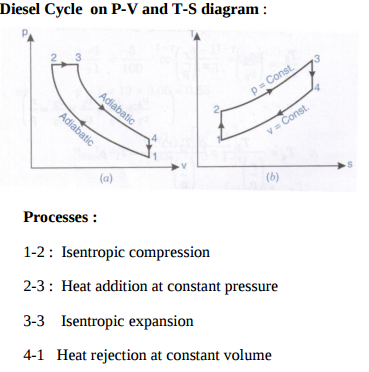
Explain construction and working of single stage reciprocating air compressor
In single stage reciprocating air compressor, the entire compression is carried out in a single cylinder. The opening & closing of a simple check valve (plate or spring valve) depends upon the difference in pressure, if mechanically operated valves are used for suction & discharge then their functioning is controlled by cams. The weight of air in the cylinder will be zero when the piston is at top dead centre. At this position, you have to neglect clearance volume.