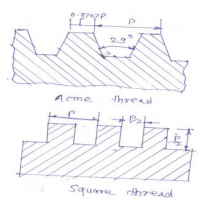
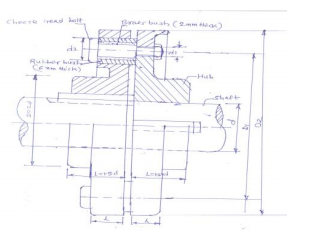
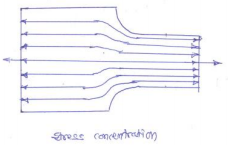
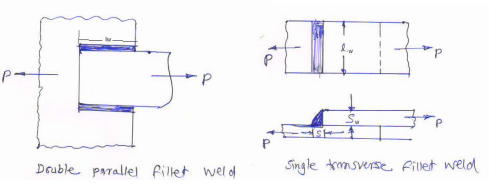
State and explain main considerations in machine design.
Main considerations in machine design Type of loads and stresses caused by the load: the load on a machine component, may act in several ways, due to which, the internal stresses are set up. Mechanism: the successful operation of any machine depends largely upon the simplest arrangement of the parts, which will give desired motion Selection of material: designer should know the deep knowledge of properties of materials and behavior under working conditions