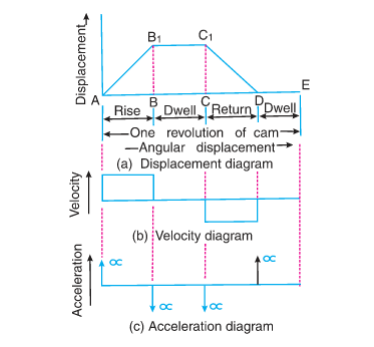
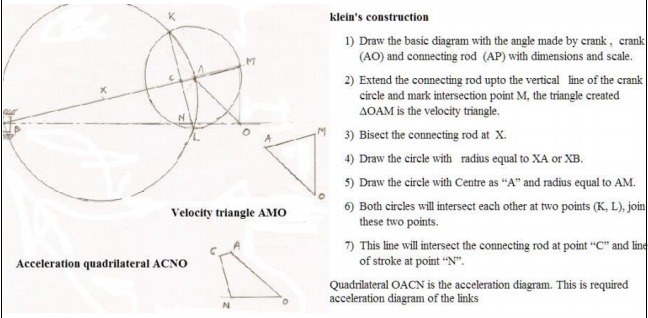
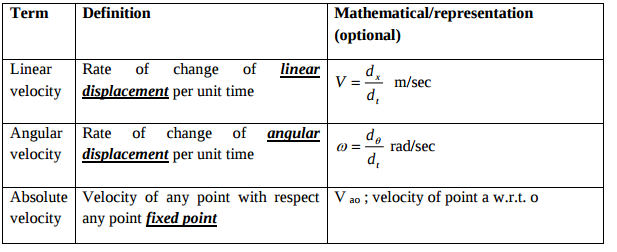
A flat belt drive is required to transmit 35 kW from a pulley of 1.5 m effective diameter running at speed of 300 rpm. The angle of contact is spread over 11/24 of the circumference co-efficient of friction for the surface is 0.3. Determine the maximum t