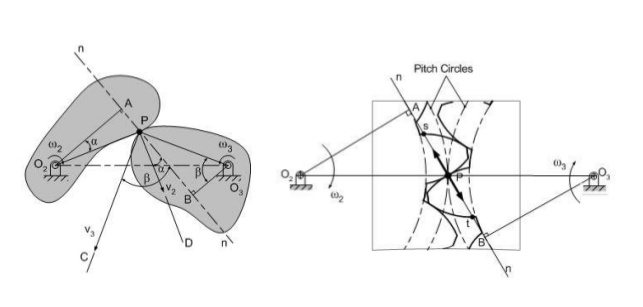
Compare brakes and dynamometers. (any two points)
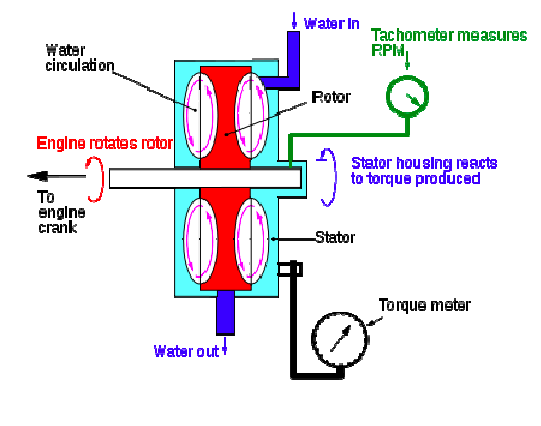
Compare Brakes & Dynamometers: A dynamometer is a mechanical device used to indirectly measure the power output of a prime mover like an engine or a motor. Examples: hydraulic brake dynamometer, eddy current dynamometer, prony brake dynamometer. A brake is a mechanical device usually found in automobiles that helps in decelerating a vehicle and brings it to a complete stop. Examples: internal expanding shoe brake, single and double shoe brake, simple and differential band brake.