CPS Question and answers
| Que.No | Question/Problem | marks | Link |
|---|---|---|---|
| Q 1 a ) |
Question:
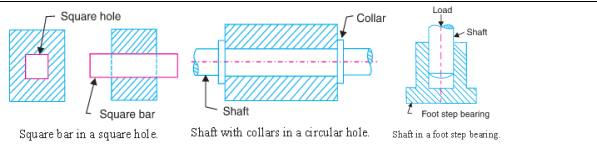
Define inversion with example. Answer:
|
2 |
view |
| Q 1 b ) |
Question:
List the inversions for double slider crank mechanism. Answer:
|
2 |
view |
| Q 1 c ) |
Question:
Define sliding pair with example. Answer:
|
2 |
view |
| Q 1 d ) |
Question:
Define centripetal and tangential acceleration. Answer:
|
2 |
view |
| Q 1 f ) |
Question:
Classify the cam. Answer:
|
2 |
view |
| Q 1 g ) |
Question:
Define following terms with respect to cam and follower : (i) Prime circle (ii) Pitch circle (iii) Pressure angle (iv) Trace point
Answer:
|
2 |
view |
| Q 1 h ) |
Question:
What are the limitations of knife edge follower ? Answer:
|
2 |
view |
| Q 1 i ) |
Question:
Define self-energizing and self-locking brake. Answer:
|
2 |
view |
| Q 1 i ) |
Question:
Write down the formula of length of belt for open belt drive and cross belt drive. Answer:
 |
2 |
view |
| Q 1 i ) |
Question:
List the methods to reduce the slip in belt and pulley. Answer:
|
2 |
view |
| Q 1 k ) |
Question:
Define law of gearing. Answer:
|
2 |
view |
| Q 1 m ) |
Question:
What are the limitations of shoe brake ? Answer:
|
2 |
view |
| Q 1 n ) |
Question:
Define uniform wear theory and uniform pressure theory. Answer:
|
2 |
view |
| Q 1 o ) |
Question:
State effects of imbalance in machine. Answer:
|
2 |
view |
| Q 2 b ) |
Question:
Explain with neat sketch how to find the velocity of a slider in slider crank mechanism by Klein’s construction. Answer:
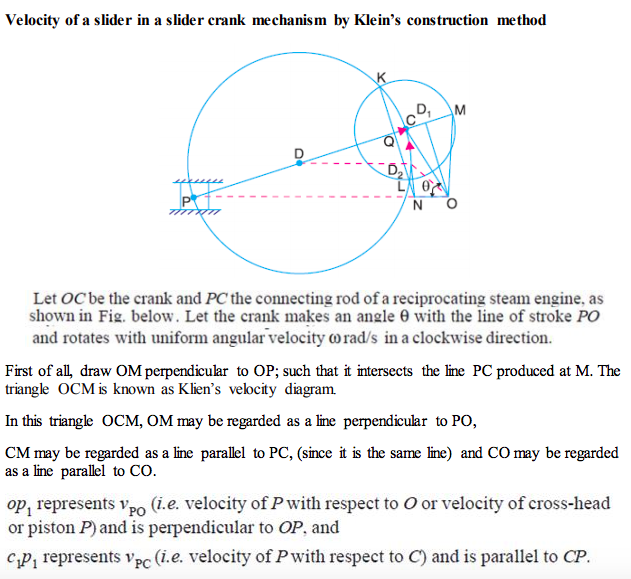 |
2 |
view |
| Que.No | Question/Problem | marks | Link |
|---|---|---|---|
| Q 1a)(a) |
Question:
Pappu Define kinematic link and kinematic chain. Answer:
|
2 |
view |
| Q 1a)(a) |
Question:
Define kinematic link and kinematic chain. Answer:
|
2 |
view |
| Q 1a)(b) |
Question:
State types of cams. Answer:
|
2 |
view |
| Q 1a)(c) |
Question:
State law of gearing. Answer:
|
2 |
view |
| Q 1a)(d) |
Question:
State the types of chains & sprockets. Answer:
|
2 |
view |
| Q 1a)(e) |
Question:
State the function of flywheel in I.C. Engine. Answer:
|
2 |
view |
| Q 1a)(f) |
Question:
State the function of governor. Answer:
|
2 |
view |
| Q 1a)(g) |
Question:
Compare brakes and dynamometers. (any two points) Answer:
|
2 |
view |
| Q 1a)(h) |
Question:
Why is balancing of rotating parts necessary for high speed engines ? Answer:
|
2 |
view |
| Q 1a)(i) |
Question:
(a) Define : (i) Spherical pair (ii) Higher pair Answer:
|
2 |
view |
| Q 1 b ) |
Question:
(b) Define : (i) Radial follower (ii) Off-set follower Answer:
|
2 |
view |
| Q 1 c ) |
Question:
What do you mean by crowning of pulleys in flat belt drive ? State its use. Answer:
|
2 |
view |
| Q 1 d ) |
Question:
Define initial tension in belt drive & state its effect. Answer:
|
2 |
view |
| Q 1 e ) |
Question:
Define fluctuation of speed and fluctuation of energy in case of flywheel. Answer:
|
2 |
view |
| Q 1 f ) |
Question:
Define the sensitivity in relation to governer. State its significance. Answer:
|
2 |
view |
| Q 1 h ) |
Question:
State the adverse effect of imbalance of rotating elements of machine. Answer:
|
2 |
view |
| Que.No | Question/Problem | marks | Link |
|---|---|---|---|
| Q 1a)(i) |
Question:
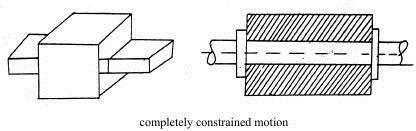
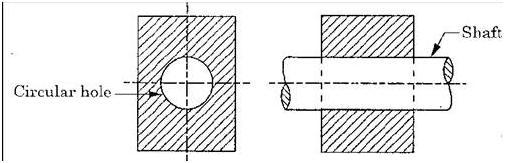
Enlist the types of constrained motion. Draw a label sketch of any one Answer:
(i)Completely constrained motion. (ii)Incompletely constrained motion. (iii)Successfully constrained motion. |
2 |
view |
| Q 1a)(ii) |
Question:
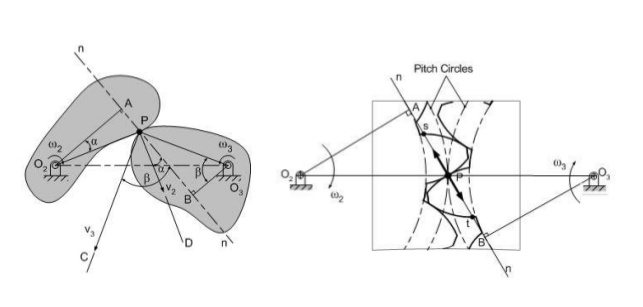
Define (i) Pressure angle (ii) Pitch point related to cam. Answer:
(ii) Pitch point: It is point on pitch curve having the maximum pressure angle. |
2 |
view |
| Q 1a)(iii) |
Question:
How are drives classified? Answer:
(i) Belt drives. (ii) Chain drives. (iii) Rope. (iv) Gear drives. |
2 |
view |
| Q 1a)(iv) |
Question:
Define: Answer:
Mathematically, C s = (N 1 – N 2 ) /N Where, N 1 = maximum speed in rpm; Mathematically, Ce = Maximum fluctuation of energy/ Work done per cycle. |
2 |
view |
| Q 1a)(v) |
Question:
Write any two disadvantages of chain drive. Answer:
1. Manufacturing cost of chains is relatively high. 2. The chain drive needs accurate mounting and careful maintenance. 3. High velocity fluctuations especially when unduly stretched. 4. Chain operations are noisy as compared to belts. |
2 |
view |
| Q 1a)(vi) |
Question:
Draw line diagram of porter governor Answer:
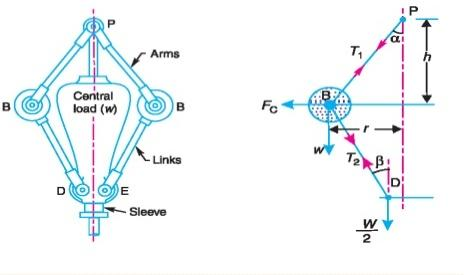 |
2 |
view |
| Q 1a)(vii) |
Question:
State the application of (i) Disc brake (ii) Internal expanding brake Answer:
(ii) Internal expanding brake: Used in motor cars, light trucks, two wheelers etc. |
2 |
view |
| Q 1a)(viii) |
Question:
Why is balancing of rotating parts necessary for high speed engines? Answer:
is, therefore, very essential that all the rotating and reciprocating parts should be completely balanced as far as possible. If these parts are not properly balanced, the dynamic forces are set up. These forces not only increase the loads on bearings and stresses in the various members, but also produce unpleasant and even dangerous vibrations. The balancing of unbalanced forces is caused by rotating masses, in order to minimize pressure on the main bearings when an engine is running. |
2 |
view |
| Que.No | Question/Problem | marks | Link |
|---|---|---|---|
| Q 1a)(i) |
Question:
Define Kinematic link with one example. Answer:
|
2 |
view |
| Q 1a)(ii) |
Question:
Name different mechanisms generated from a single slider crank chain. Answer:
|
2 |
view |
| Q 1a)(iii) |
Question:
State the advantages of roller follower over knife edge follower. Answer:
|
2 |
view |
| Q 1a)(iv) |
Question:
Define slip and creep in case of belt drive. Answer:
|
2 |
view |
| Q 1a)(v) |
Question:
Give four advantages of chain drive over belt drive. Answer:
|
2 |
view |
| Q 1a)(vi) |
Question:
State the effect of centrifugal tension on power transmission. Answer:
|
2 |
view |
| Q 1a)(vii) |
Question:
Define fluctuation of energy and coefficient of fluctuation of energy. Answer:
|
2 |
view |
| Q 1a)(viii) |
Question:
State the adverse effect of imbalance of rotating elements of machine. Answer:
|
2 |
view |
| Que.No | Question/Problem | marks | Link |
|---|---|---|---|
| Q 1a)(a) |
Question:
Define kinematic link and kinematic chain. Answer:
|
2 |
view |
| Q 1a)(b) |
Question:
Enlist the different type of follower motion. Answer:
|
2 |
view |
| Q 1a)(c) |
Question:
Define angle of lap and slip in belt drive. Answer:
|
2 |
view |
| Q 1a)(d) |
Question:
State four conditions under which the ‘V’ belt drive is selected. Answer:
|
2 |
view |
| Q 1a)(e) |
Question:
State the function of Governor in an I.C. engine. Answer:
|
2 |
view |
| Q 1a)(f) |
Question:
State four applications of flywheel. Answer:
|
2 |
view |
| Q 1a)(g) |
Question:
Give the classification of dynamometer. State the function of it. Answer:
|
2 |
view |
| Q 1a)(h) |
Question:
Why is balancing of rotating parts necessary for high speed engines ? Answer:
|
2 |
view |
| Que.No | Question/Problem | marks | Link |
|---|---|---|---|
| Q 1a)(i) |
Question:
Define - 1. Mechanism 2.Inversion Answer:
|
2 |
view |
| Q 1a)(ii) |
Question:
State any two types of motion of the follower.
Answer:
|
2 |
view |
| Q 1a)(iii) |
Question:
Define slip and creep in the belt. Answer:
|
2 |
view |
| Q 1a)(iv) |
Question:
State any two advantages of V belt drive over flat belt drive. Answer:
|
2 |
view |
| Q 1a)(v) |
Question:
State the function of flywheel in IC engine. Answer:
|
2 |
view |
| Q 1a)(vi) |
Question:
Define stability and hunting of governor. Answer:
|
2 |
view |
| Q 1a)(vii) |
Question:
Compare brakes and dynamometers (two points). Answer:
|
2 |
view |
| Q 1a)(viii) |
Question:
State any two adverse effects of imbalance. Answer:
|
2 |
view |
| Q 1b)(i) |
Question:
Draw neat labeled sketch of crank and slotted lever mechanism. Label all parts. Answer:
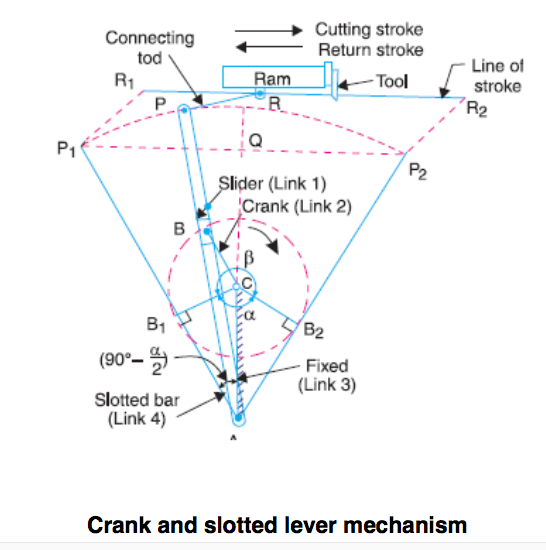 |
2 |
view |
| Q 1b)(ii) |
Question:
What is the necessity of clutch? State its types. Answer:
|
2 |
view |